
Primary control block diagram of an inverter-based Distributed
In order to facilitate the integration of DGs, loads, and energy storage systems for meeting the energy demand, microgrids (MGs) are built as suitable and flexible platforms [5] [6] [7]. The

Stability Control of Energy Storage Voltage Source Inverters in
provide support for the voltage, the energy-storage power source inverter needs an method to control the voltage source. Therefore, this paper has proposed the active damping control of a
Battery energy storage systems (BESS) frequency regulation block diagram.
Download scientific diagram | Battery energy storage systems (BESS) frequency regulation block diagram. from publication: Voltage/Frequency Deviations Control via Distributed Battery

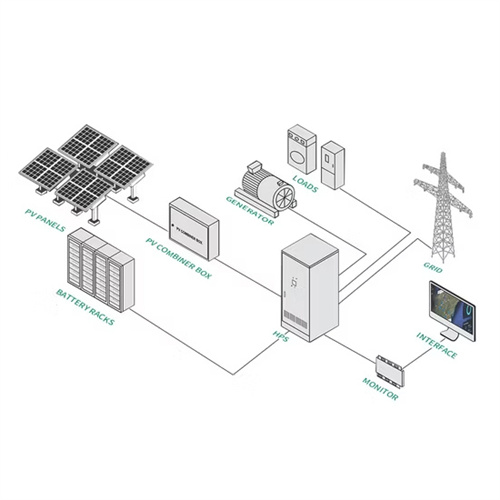
Solar Power Inverter Block Diagram Explained – solar
A solar power inverter is an essential component of a solar energy system that converts the DC (direct current) electricity generated by solar panels into AC (alternating current) electricity. Understanding the block

An improved energy storage switched boost
This paper proposes an energy storage switch boost grid-connected inverter for PV power generation systems. The system has the ability of energy storage and PV power generation to work together, as well as high

Modelling, control and performance analysis of a single‐stage
Under this condition, two-stage inverter will have the same control block diagram and transfer function expressions with the single-stage ones, which are shown in Fig. 4b, –.

Block diagram of an inverter with closed-loop voltage feedback control
Download scientific diagram | Block diagram of an inverter with closed-loop voltage feedback control. To realise the distributed control of the hybrid energy storage system (HESS) in an

Bidirectional Operation Scheme of Grid-Tied Zeta Inverter for Energy
The zeta inverter has been used for single-phase grid-tied applications. For its use of energy storage systems, this paper proposes the bidirectional operation scheme of the

Frequency Dynamics with Grid Forming Inverters: A New
output, although here an energy storage system with available energy is assumed for simplicity 2dot notation indicates time derivative; x_ = d dt export relationship. For this work, we focus on

The inverter block diagram. | Download Scientific
Different inverter topology and various sophisticated control methodologies like zero crossing based phase synchronous inverter for sustainable energy are studied in detail in [2] to integrate

Inverter-based islanded microgrid: A review on technologies and control
The block diagram of the inverter is shown in Fig. 2. Inverters are classified into many different categories based on the applied input source, Research on energy control of

Control and Intelligent Optimization of a Photovoltaic
The block diagram for the three-phase grid-connected inverter''s V/F control is shown in Figure 6. In V/F control, the inverter output voltage is directly controlled [ 36 ]. The internal current loop is typically set up within the

Block diagram of an EV off-board charging station including energy
Download scientific diagram | Block diagram of an EV off-board charging station including energy storage (ES) and PV panels based on the multiport inverter. from publication: A

Control principles of micro-source inverters used in microgrid
GFM inverters usually equips with energy storage on their DC sides, therefore they can respond to the change of load in a short time. The control block diagram of a GFM inverter is shown in

AC/DC, DC-DC bi-directional converters for energy storage
systems (PCS) in energy storage Bi-Directional Dual Active Bridge (DAB) DC:DC Design 20 • Single phase shift modulation provides easy control loop implementation. Can be extended to

10-kW, GaN-Based Single-Phase String Inverter With Battery
to renewable energy further and making solar energy more accessible for residential purposes. The modularity of string inverters, low cost-per-watt and easy amplification to attain higher

Control block diagram of three-phase grid-forming inverter
Download scientific diagram | Control block diagram of three-phase grid-forming inverter from publication: Control principles of micro-source inverters used in microgrid | Since micro

Control and Intelligent Optimization of a Photovoltaic (PV) Inverter
The block diagram for the three-phase grid-connected inverter''s V/F control is shown in Figure 6. Mahmud, N.; Zahedi, A.; Mahmud, A. A Cooperative operation of novel
6 FAQs about [Control block diagram of energy storage inverter]
How do inverters affect a grid-connected PV system?
For a grid-connected PV system, inverters are the crucial part required to convert dc power from solar arrays to ac power transported into the power grid. The control performance and stability of inverters severely affect the PV system, and lots of works have explored how to analyze and improve PV inverters’ control stability .
What is constant power control in a PV inverter?
In general, PV inverters’ control can be typically divided into constant power control, constant voltage and frequency control, droop control, etc. . Of these, constant power control is primarily utilized in grid-connected inverters to control the active and reactive power generated by the PV system .
How do PV inverters control stability?
The control performance and stability of inverters severely affect the PV system, and lots of works have explored how to analyze and improve PV inverters’ control stability . In general, PV inverters’ control can be typically divided into constant power control, constant voltage and frequency control, droop control, etc. .
What is the control performance of PV inverters?
The control performance of PV inverters determines the system’s stability and reliability. Conventional control is the foundation for intelligent optimization of grid-connected PV systems. Therefore, a brief overview of these typical controls should be given to lay the theoretical foundation of further contents.
How Ann control a PV inverter?
Figure 12 shows the control of the PV inverters with ANN, in which the internal current control loop is realized by a neural network. The current reference is generated by an external power loop, and the ANN controller adjusts the actual feedback current to follow the reference current. Figure 12.
What is inverter-based MG control design?
Inverter-based MG control design plays an important role in influencing the dynamic performance of the system. Inverter-based MG operates in either grid-connected or islanded mode. Their control architectures are currently designed with droop-based control, active power connection to frequency and reactive power to voltage [141, 142].