
What Are the Differences Between Horizontal-axis Wind Turbine
Horizontal Axis Wind Turbines (HAWTs) have their axis of rotation parallel to the ground, making them optimal for capturing stronger winds at higher altitudes. In contrast, Vertical Axis Wind Turbines (VAWTs) feature a vertical axis, beneficial in environments with variable wind directions and lower wind speeds.

Horizontal Axis Wind Turbine | PPT
• Controller – The controller starts up the machine at wind speeds of about 8 to 16 miles per hour (mph) and shuts off the machine at about 55 mph. – Turbines do not operate at wind speeds above about 55 mph because they might be damaged by the high winds – The controller gets wind speed data from the anemometer and acts accordingly .

Horizontal Axis Wind Turbine | PPT
• Controller – The controller starts up the machine at wind speeds of about 8 to 16 miles per hour (mph) and shuts off the machine at about 55 mph. – Turbines do not operate at wind speeds above about 55 mph

DESIGN AND FABRICATION OF HORIZONTAL AXIS WIND
to maximise the wind turbine''s rotating speed. To get electricity, a DC dynamo that serves as a generator is employed. Keywords: Renewable sources, Horizontal Axis Wind Turbine, wind Energy, hub, blade, fabrication, Gear Ratio, Dynamo. I. INTRODUCTION Like the majority of forms of energy on Earth, wind energy is created by solar energy.

Environmental Feasibility of Offshore Wind Farms for
A mesoscale meteorological model was then used at high horizontal resolution (5 and 1.67 km) to calculate annual 80 m wind speeds (turbine hub height) for each area, based on the average of...
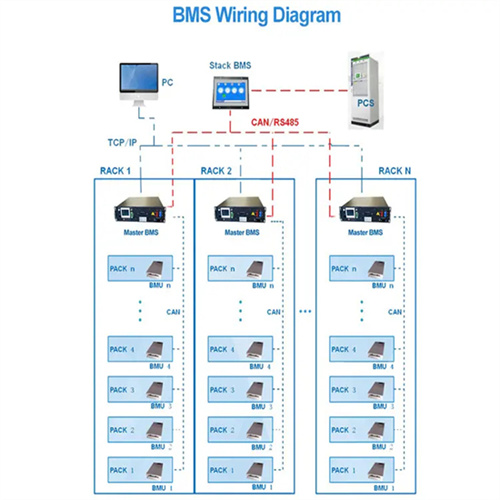
Horizontal-Axis Wind Turbine (HAWT) Working Principle | Single
Horizontal-axis wind turbines may produce less than 100 kW for basic applications and residential use or as much as 6 MW for offshore power generation. Even larger turbines are on the drawing board. Horizontal-Axis Wind Turbine Working Principle. The horizontal-axis wind turbine (HAWT) is a wind turbine in which the main rotor shaft is pointed

Comparison between horizontal and vertical axis wind turbine
The vertical axis wind turbine (VAWT) design was invented for working conditions, capacities, and places, in which it may be difficult to install older Horizontal axis wind turbines (HAWT).

Exploring The Advantages And Disadvantages Of Horizontal Axis Turbines
Enhanced Performance in Low Wind Speeds: Horizontal axis turbines have demonstrated better performance in low wind speeds compared to vertical axis turbines. This advantage allows for power generation even in areas where wind speeds may not be consistently high. 4. Scalability: Horizontal axis turbines can be scaled up to larger sizes, making

10kW Wind Turbine
Type: 10kW horizontal wind turbine. Price Term: EXW. Can work with solar/battery/grid or generator backup. Get Total Price. Introduction of 10kW Wind Turbine. PVMARS''s horizontal axis wind turbines have tail rudders. These rudders
Wind Energy at Home: How to Choose Between
A Horizontal Axis Wind Turbine, often referred to as HAWT, is a powerful and efficient wind energy generator. It features a familiar design with its rotor shaft and blades rotating horizontally, capturing the kinetic energy of

Difference Between Horizontal and Vertical Axis Wind Turbine
– The horizontal axis wind turbines have the entire rotor, gearbox and generator mounted at the top of the tower, which must be turned to face the wind direction. A significant advantage of vertical axis wind turbine over horizontal axis type is that the former can accept wind from any direction and thus no yaw control is needed. In VAWTs

Horizontal Axis Wind Turbine: Working Principle
Horizontal Axis Wind Turbine. We consider HAWT upwind turbines with three blades. This configuration is the most popular commercially. The more the number of blades, the slower the rotor speed. So, turbines with 3 blades are relatively slower but will gain a high efficiency and a high torque.

Multidisciplinary dynamic optimization of horizontal axis wind turbine
The operating regimes for wind turbine systems have traditionally been categorized into three operational zones (ref. Fig. 2), Zone 1: below cut-in wind speed (i.e., speeds below the minimum required to produce useful power), Zone 2: between cut-in and rated wind speeds, Zone 3: between rated and cut-out speed (cut-out speed is the speed at which

Analysis of Performance and Optimization Strategies for Horizontal Axis
This research paper represents a comprehensive review of horizontal axis wind turbines (HAWTs), focusing on their design and performance analysis. HAWTs are one of the most widely used

Performance and wake measurements on a 3 m diameter horizontal axis
Comparison of theory, wind tunnel and field test data} author = {Anderson, M B, Milborrow, D J, and Ross, J N} abstractNote = {A 3 m diameter horizontal axis wind turbine rotor has been tested in a large wind tunnel and in the field and the results are compared with theoretical predictions. The size of the rotor was chosen to obtain the most

Types of Wind Turbines: HAWT, VAWT and More Explained
The most common type of wind turbine is the ''Horizontal Axis Wind Turbine'' (HAWT). It is referred to as a horizontal axis as the rotating axis lies horizontally (see diagram, below). A HAWT needs to point directly into the wind to operate at maximum efficiency, and the whole head is designed to turn to face the wind.

Wind energy added to Trinidad and Tobago''s
Planning and Development Minister Pennelope Beckles-Robinson says wind energy is a promising solution to meet TT''s growing energy demands by mitigating greenhouse gas emissions. She was speaking at the

Setting the Path for Wind Energy Generation in
In order to fulfill Trinidad and Tobago''s expanding energy needs while reducing greenhouse gas emissions, wind energy has emerged as a possible answer. An exceptional opportunity to access a clean and almost

Comparison between horizontal and vertical axis wind
horizontal axis wind turbines (HAWT) [12]. 14 ISSN: 2252-8792 Int J Appl Power Eng, Vol. 12, No. 1, March 2023: 13-23 The aim of this comparison is to determine the basic differences between the
Vertical Axis Marine Current Turbine Modelling
horizontal-axis turbine can capture more tidal energy but requires a control device to direct it in the direction of the oncoming current. In comparison to natural gas-fired power Winds are a strong wind that blows across Trinidad and Tobago, contributing to the presence of waves around the islands, and allowing offshore energy farms to be

Vertical Axis Wind Turbine Market Size, Share | Forecast 2032
The Global Vertical Axis Wind Turbine (VAWT) Market Size accounted for USD 12.9 Billion in 2022 and is projected to achieve a market size of USD 17.7 Billion by 2032 growing at a CAGR of 3.2% from 2023 to 2032.

What are Horizontal Axis Wind Turbine Types?
After understanding horizontal axis wind turbine types, let''s also learn about the horizontal axis wind turbine working principle. Wind power is c onverted into torque by the rotor, which is then transmitted to a slow-moving shaft.

Wind Energy Production from Vertical Axis Wind Turbine on
Results: The modeled vertical axis wind turbine monthly total power output varied from 5.43 KW to 20.34 KW. The daily average expected power output from the VAWT ranged from 175 Watts to 678 Watts.

Vertical Axis Wind Turbine Market Trends
Vertical Axis Wind Turbine Market by Type (darrieus and savonius), End-User (residential, commercial and industrial, fishery and recreational boats, hybrid systems, pastures, farms and remote villages, potable systems for leisure, pumping, desalination and purification, remote monitoring, and research and education), and Region (North America, Europe, Asia Pacific,

Review of Analysis on Vertical and Horizontal Axis Wind Turbines
Wind turbine is a device used to convert kinetic energy into electrical energy. Generally, wind turbine could be classified as horizontal axis and vertical axis wind turbine, depending on its axis

Comparative Study on Horizontal Axis Wind Turbines and
1.3 Horizontal axis wind turbine 05 1.4 Vertical axis wind turbine 05 2.1 Overview of history of wind energy 06 2.2 Block Diagram of Wind Turbine 09 3.1 Swept area of HAWT 09 3.2 Modified lift and

Vertical Axis Wind Turbines vs. Horizontal Axis: Which
Wind energy has emerged as a crucial player in the global transition towards sustainable power sources. Among the various types of wind turbines, two designs stand out: vertical axis wind turbines (VAWTs) and horizontal axis

10kW Wind Turbine
Type: 10kW horizontal wind turbine. Price Term: EXW. Can work with solar/battery/grid or generator backup. Get Total Price. Introduction of 10kW Wind Turbine. PVMARS''s horizontal axis wind turbines have tail rudders. These

Total-to-static efficiency and horizontal-axis wind turbine design
@misc{etde_20042222, title = {Total-to-static efficiency and horizontal-axis wind turbine design} author = {Ntoko, N-M} abstractNote = {It is shown that the total-to-static efficiency used in axial-flow-turbine theory is equivalent to the coefficient of performance of horizontal-axis wind turbines. After showing the relationship between efficiency and stage loading factor, a

Kinematically nonlinear finite element model of a horizontal axis wind
@misc{etde_10110609, title = {Kinematically nonlinear finite element model of a horizontal axis wind turbine. Part 1. Mathematical model and results} author = {Thirstrup Petersen, J} abstractNote = {A mathematical time domain model for simulation of the dynamic response of a horizontal axis wind turbine is presented. The model concentrates on the correct
3 FAQs about [Trinidad and Tobago wind turbine horizontal axis]
How much power can a vertical axis wind turbine produce?
As estimated by a previous study, in general, a vertical axis wind turbine having a blade area of 5 × 8 m can be well-integrated into a building and produce a maximum power output of 36 kW under a wind speed of 15 m/s .
What are the challenges and emphases of wind turbine advancement?
The improvement in energetic conversion efficiency is considered among the biggest challenges and emphases of wind turbine advancement in the wind power industry. At present, horizontal-axis turbines offer high efficiencies, and they convert 40%–50% of wind energy into electricity.
What is the coefficient of airfoil in a horizontal axis wind turbine?
Airfoils for horizontal axis wind turbines (HAWTs) often coefficients are fairly low. The li ft coefficient of this symmetric airfoil is about zero at an angle of attack of zero and increases to over 1.0 before decreasing at higher angles of att ack. The drag coefficient is usually much lower than the lift coeff icient at low ang les of attack.