
(PDF) Preliminary analytical study on the feasibility of
Reinforced concrete pile foundations have been proposed for renewable energy storage by utilizing compressed air energy storage (CAES) technology [3, 4]. The pile foundation is designed with a
Underground Gravity Energy Storage: A Solution for
Low-carbon energy transitions taking place worldwide are primarily driven by the integration of renewable energy sources such as wind and solar power. These variable renewable energy (VRE) sources require energy

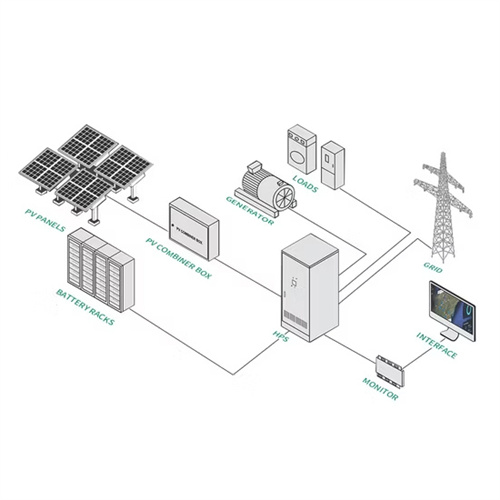
Battery Energy Storage Systems (BESS) – RRC Companies
Battery Energy Storage System RRC delivers Battery Storage solutions that are optimized to the requirements of each site. RRC is unique in its ability to bring both engineering and on-site

Energy storage in the geological subsurface:
Enhanced numerical tools enable the computation of coupled thermal (T), hydraulic (H), mechanical (M) and chemical (C) processes (THMC-processes) induced by geotechnical energy storage operations for realistically
6 FAQs about [Geotechnical energy storage technology]
How do geotechnical engineers work with energy storage?
Geotechnical engineers have been involved with energy storage through the design of reservoirs for pumped-hydro energy storage, where water is pumped to a reservoir with higher elevation during times when electricity costs are low, and electricity is generated through hydro-power.
How can thermal energy storage be adapted in geological settings?
The storage of mechanical energy in the form of compressed air in subsurface caverns or aquifers is another innovative technique that can be adapted in many geological settings , , [*291]. Most underground thermal energy storage systems involve storage of heat at temperatures between 50 and 95 °C .
What is used subsurface space in Geotechnical Energy Storage?
Three categories of used subsurface space have been identified and developed in the ANGUS+ project in the context of geotechnical energy storage: firstly, the “operational space” (Fig. 2 ), i.e., the space directly used by the storage operation, which comprises the technical installations and the space taken up by the injected gas or heat.
Can geological reservoirs be used for energy storage?
Electric energy storage technologies, involving the use of geological reservoirs offer large storage capacities and discharge rates [ 6 ], bringing all the advantages of a large-scale energy storage system while minimising environmental and social impacts, and the need for surface space.
What is underground thermal energy storage (SHS)?
SHS can be developed at a small-scale (<10 MW) above surface technology or at a large-scale system in the subsurface. Underground Thermal Energy Storage (UTES) is a form of energy storage that provides large-scale seasonal storage of cold and heat in underground reservoirs [ 74, 75, 76, 77 ].
What is energy geotechnics?
An underlying theme among the different topics within Energy Geotechnics is the need to predict the flow of fluids and transfer of heat in porous or fractured media, and understand the coupled role of, or impacts on, the mechanical response of the media (i.e., volume change, changes in stiffness, changes in strength).